Broker 0.1 spread means
Zero spread accounts offer small traders the chance to compute their executions precisely, without the issue of tightening or widening of spreads.
Top forex bonuses
The two most important categories in our rating system are the cost of trading and the broker’s trust score. To calculate a broker’s trust score, we take into account a range of factors, including their regulation history, years in business, liquidity provider etc.
Compare zero spread brokers
For our zero spread accounts comparison, we found 5 brokers that are suitable and accept traders from united states of america.
We found 5 broker accounts (out of 147) that are suitable for zero spread accounts.
Thinkmarkets
Spreads from
What can you trade?
- Forex
- Crypto currencies
- Indices
- Commodities
- Stocks
- Etfs
About thinkmarkets
Platforms
Funding methods
Losses can exceed deposits
Between 54-87% of retail CFD accounts lose money. Based on 69 brokers who display this data.
The ultimate guide to
Using zero spread accounts in forex trading
Zero spread accounts are trading accounts offered by brokers that have no difference between the bid and ask price. Such accounts allow traders to know in advance what their entry and exit levels will be when they open positions.
Zero spread accounts are also helpful for calculating non-trading losses, such as slippage, and are ideal for some forex strategies including high-frequency scalping and day trading.
When forex brokers started offering their services, they touted their low spreads and low commission rates as their primary marketing tools. However, with the advent of electronic communication network (ECN) brokers and straight through processing (STP) brokers competing for best price, zero spread accounts became the newest trending marketing tool forex brokers used to entice potential traders.
Advantages of zero spread accounts
Zero spread accounts offer small traders the chance to compute their executions precisely, without the issue of tightening or widening of spreads.
For example, when trading on the wrong side of the move of a USD/JPY during a big fundamental data release, like the rate decision of the bank of japan, having a zero spread account would allow traders to change their trade bias accordingly, without the additional damage to their trading account caused by a spiking forex spread (which could be more than 300 pips greater than a normal spread) on a normal forex account.
Disadvantages of zero spread accounts
However, there are disadvantages to zero spread accounts. Forex brokers also have to make money in various other ways. These brokers might offer fixed commissions (thus, simulating the fixed spread accounts), smaller/bigger leverage, bigger initial account opening size, slightly slower execution speeds, non-application of negative balance protection, tighter margin calls and stop loss levels, or various permutations of the above mentioned tactics.
How to compare brokers that offer zero spread accounts
One of the first things to look out for when comparing zero spread account brokers is how much commission they charge. Some brokers charge a nominal commission or fee, as well as adding a small markup to the spreads, whilst claiming to be zero spread brokers.
There are also brokers who offer zero spreads without commission. They tend to be dealing desk brokers who do not send clients’ positions into the open market (liquidity providers).
Conclusion
In conclusion, zero spread forex trading offers new traders the opportunity to try out currency trading without being exposed to high transaction costs.
However, the milton friedman’s economic principle that “there is no such thing as a free lunch” also applies to the forex market, and especially to zero spread accounts. Traders therefore need to examine commission, fees, and tactics employed by the broker that may provide them with the opportunity to make money from their clients.
Why choose thinkmarkets
for zero spread accounts?
Thinkmarkets scored best in our review of the top brokers for zero spread accounts, which takes into account 120+ factors across eight categories. Here are some areas where thinkmarkets scored highly in:
- 8+ years in business
- Offers 50+ instruments
- A range of platform inc. MT4, mac, web trader, tablet & mobile apps
Thinkmarkets offers two ways to tradeforex, cfds. If you wanted to trade EURUSD
The two most important categories in our rating system are the cost of trading and the broker’s trust score. To calculate a broker’s trust score, we take into account a range of factors, including their regulation history, years in business, liquidity provider etc.
Thinkmarkets have a AAA trust score. This is largely down to them being regulated by financial conduct authority and ASIC, segregating client funds, being segregating client funds, being established for over 8
Trust score comparison
| thinkmarkets | |
|---|---|
| trust score | AAA |
| established in | 2010 |
| regulated by | financial conduct authority and ASIC |
| uses tier 1 banks | |
| company type | private |
| segregates client funds |
A comparison of thinkmarkets
Want to see how thinkmarkets? We’ve compared their spreads, features, and key information below.
Spread & fee comparsion
Comparison of account & trading features
| thinkmarkets | |
|---|---|
| platform | MT4, mac, web trader, tablet & mobile apps |
| services | forex, cfds |
| base currency options | USD, GBP, EUR, CHF, JPY, SGD, AUD, CAD, NZD, CNH |
| funding options | payoneer, credit cards, bank transfer, neteller, BPAY, unionpay, fasapay, debitcard, |
| micro account | |
| ECN account |
Frequently asked questions
Related pages
Ready to find your broker?
Brokernotes ltd is an appointed representative of resolution compliance ltd, which is authorised and regulated by the financial conduct authority (FRN: 574048). Brokernotes ltd is registered in england and wales. Company no. 10464674. Registered office: thames wing, howbery park, wallingford, OX10 8BA, UK.
What does a forex spread tell traders?

Forex spreads explain ed : main t alking points
- Spreads are based on the buy and sell price of a currency pair.
- Costs are based on forex spreads and lot sizes.
- Forex spreads are variable and should be referenced from your trading platform.
It’s important for traders to be familiar with FX spreads as they are the primary cost of trading currencies. In this article we explore how forex spreads work, and how to calculate costs and keep an eye on changes in the spread to maximize your trading success.
What is a spread in forex trading?
Every market has a spread and so does forex . A spread is simply defined as the price difference between where a trader may purchase or sell an underlying asset. Traders that are familiar with equities will synonymously call this the bid: ask spread.
Below we can see an example of the forex spread being calculated for the EUR/USD . First, we will find the buy price at 1.13398 and then subtract the sell price of 1.3404 . What we are left with after this process is a reading of .00006 . Traders should remember that the pip value is then identified on the EUR/USD as the 4th digit after the decimal, making the final spread calculated as 0.6 pips.
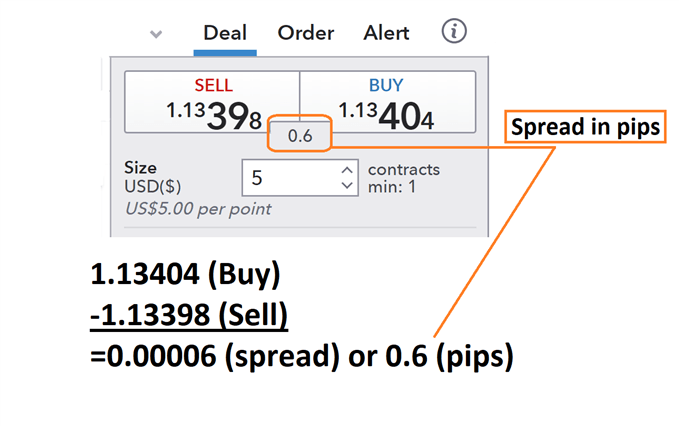
Now we know how to calculate the spread in pips, let’s look at the actual cost incurred by traders.
How to calculate the forex spread and costs
Before we calculate the cost of a spread, remember that the spread is just the ask price less (minus) the bid price of a currency pair. So, in our example above, 1.13404-1.13398 = 0.00006 or 0.6 pips.
Using the quotes above, we know we can currently buy the EUR/USD at 1.13404 and close the transaction at a sell price of 1.13398. That means as soon as our trade is open, a trader would incur 0.6 pips of spread.
To find the total spread cost, we will now need to multiply this value by pip cost while considering the total amount of lots traded. When trading a 10k EUR/USD lot, you would incur a total cost of 0.00006 (0.6pips) X 10,000 (10k lot) = $0.6. If you were trading a standard lot (100,000 units of currency) your spread cost would be 0.00006pips (0.6pips) X 100,000 (1 standard lot) = $6.
If your account is denominated in another currency, like GBP, you would have to convert it to US dollars.

Understanding a high spread and a low spread
It’s important to note that the FX spread can vary over the course of the day, ranging between a ‘high spread’ and a ‘low spread’.
This is because the spread can be influenced by multiple factors like volatility or liquidity. You will notice that some currency pairs, like emerging market currency pairs , have a greater spread than major currency pairs . Your major currency pairs trade in higher volumes compared to emerging market currencies, and higher trade volumes tend to lead to lower spreads under normal conditions.
Additionally, it’s well known that liquidity can dry up and spreads can widen in the lead up to major news events and in between trading sessions .
Email was send successfully!
Please check your inbox for
our authentication email.
Thank you for registering
to finance magnates.
Please open the email we
sent you and click on the
link to verify your account.
What is a spread and why does it matter?
It’s very important to understand spreads in the FX market, as brokers can manipulate spreads on their trading platforms.

In the forex market, a spread is the difference in pips between the BID price and the ASK price quote (buy/sell) in a currency pair such as the EUR/USD. A spread is also the easiest way for many brokers to get compensated for each transaction the customer makes through their trading platforms. This is the simplest way to understand what a spread is: EUR/USD is priced at 1.1500 the broker will offer it for 1.1501 to buy or sell at 1.1499.
The trading price for any currency pair is expressed by the combination of the symbols that make up the currency pair as well as the bid and ask price. It’s expressed as follows:
Base currency/currency trading | bid price/ask price
If at any point the quote for the euro against the US dollar is 1.1500 – 1.1502 it reads as follows:
The BID is the highest the trader is willing to buy, also known as purchase price or demand. It is the price at which the trader will enter the market when selling the currency pair. The ask is the minimum price you are willing to sell, also known as selling price or supply. It is the price which the trader will enter the market when buying the currency pair.
The difference between BID and ASK is best known as the spread. The spread is expressed as pips or points. In this example, the spread in the EUR/USD is 2 pips or points.
Cost for each transaction
The spread is the cost of each transaction performed by the trader in the market (not including any other fees such as swap or commission). This cost can vary from broker to broker. There are brokers that use the market maker and ECN system which allows them to charge a very tight spread but charge commission for every transaction executed. The spread is the basic compensation for each broker and other third parties if applicable. These third parties are introducing brokers and/or money managers, who can also get compensated for their services through the spread.
How does the spread work?
Let’s follow this example: trader X wants to open a buy position in EUR/USD at a price of 1.2001. Immediately, the broker executes the order and most likely executed the order at 1.1999, instantly making 1 pip on the execution. Now trader X wants to close the buying position and sell at 1.2010, but then the broker will most likely execute the order at 1.2011 to make another pip on the execution.
In the example above, the trader encounters a fee for every execution in order to trade the forex market, in order to obtain profits from every transaction. The expectation from each trade should be over the spread amount to capitalize on every trade. In each currency pair the cost of spread is different and also the trader should account for those variables in order to make more money than the actual spread cost.
Suggested articles
FBS copytrade launches a new card scanning feature!Go to article >>
Know your spread
It’s very important to know the spread in the forex market. The spread is the cost of each transaction that the broker charges and determines if that cost is appropriate for your trading style.
Secondly, all investors and traders should be educated about the lack of information regarding the possibility of manipulating the spreads on their trading platforms without the consent of their clients. On certain occasions there are unscrupulous brokers which exercise this practice to obtain more profits. Therefore it’s essential that the trader selects a quality broker with a good reputation and that is not guilty of any spread manipulation. It is also advisable to trade with a broker regulated by a regulatory body since their regulator requires companies to meet strict requirements regarding the financial products and services such as the safety of clients’ funds in segregated accounts.
Even if you work with brokers that do not engage in any tampering, let’s go back to the importance of the spread as it represents the cost to the trader. A trader that trades with low spreads will have less operating cost and long-term savings. Therefore, a high spread trader will have to generate higher profits to offset the cost. For many traders, the spread is very important within their losses and gains. For example, if a trader makes many short-term (scalper) trades a high spread can result in absorbing most of their profits. For a long-term trader (swing) in which each trade generates a certain amount of pips in profit, the spread is a matter of little relevance since it has little impact on the results of the trading.
How to select the best broker?
At the time of selecting the best forex broker, you must take into account several criteria including the spread. The spread is a cost factor for the trader and the more you trade the more you are hit with the cost. This applies specially to those scalper traders mentioned before. A low or institutional spread broker is the answer for any scalper in order to get the best fee out there.
STP brokers also offer a good spread base on their liquidity providers although market maker brokers are always in your counterpart, they can often offer fixed spreads during certain trading hours which can be an advantage for certain traders.
Also, as mentioned in the previous section, another recommendation is to select a broker that has a good reputation without allegations or complaints of fraudulent dealings. If the broker is regulated, even better, since it brings a certain level of security to the client’s money through safety of funds in segregated bank accounts.
-if you trade frequently on the forex market you should select a broker that charges the lowest spread
-avoid brokers with a bad reputation especially in the manipulation of prices
-A regulated broker offers a higher level of security to the trader regarding the company’s practices.
Email was send successfully!
Please check your inbox for
our authentication email.
Thank you for registering
to finance magnates.
Please open the email we
sent you and click on the
link to verify your account.
Beware of brokers offering zero spread!
Newfx pulppromotion– trade with ZERO spread AND ZERO margin. Opa! So you are asking yourself what’s wrong with not paying


So you are asking yourself what’s wrong with not paying for trading? The answer is simple: everything is wrong. In this cruel and competitive brokers’ world – nothing is for free, so if something is offered completely for free you should ask yourself why?
The answer is given by FX pulp right away: we are the only broker that lets you gamble with your money AND lose more than you invested. Yes that’s what ZERO margin means my friends: “we give YOU the opportunity to be left with ZERO money and pay ZERO commission for that opportunity ;)”…
ZERO spread also means that the broker makes money in other ways: FX pulp to the best of my knowledge is a market maker, therefore it makes money from trader losses as well (nothing wrong with that in general: it’s legal everywhere including the US, but that’s something you should know).
Not only that, FX pulp is also limiting the profit you can make: no less than 35 pips and no more than 100 for major currencies, so that means you’ll need to leave the position open until you are in that range = more chances to lose it all…
Here’s the full “promotion”:
ZERO margin requirements,
Suggested articles
FBS copytrade launches a new card scanning feature!Go to article >>
Our basic philosophy in zero accounts is to reduce trading costs to the minimum, or shall we say to zero, and the spread was one of the main challenges that FXPULP experts faced. Taking the spreads to 3 pips, 2 or even 1 pip sounds good at first… but how about taking it completely down to zero. Yes imagine you are trading FOREX with ZERO SPREAD the main objective from taking the spread to as low as nothing is for you dear investor, enabling you to take advantage from every pip in the market, the profits start from the first pip, you don’t need some points to cover your spreads and others for the commissions, what you get is each and every pip the market gives.
What are ZERO margin requirements?
A margin is an amount held and blocked from your account equity in order to be able to place your trades in the market.Zero margin requirements means that no money will be held and blocked in your account as margin for the trades you place; and you will be able to invest in the financial market even if your account balance is less than what is required to cover your trades as margin. We will provide you with the margin you need to take as much positions as you want; you only have to pay to cover any losses resulting from the given trades, or get paid for the resulted profits.
Normally; investors deposit money in the trading accounts which will be blocked for each trade according to the size, and the required margin, usually determined by the leverage that the broker offers.
The below table demonstrates the customary required margins:
| Leverage | required margin per contract |
| 1:100 | 1000$ |
| 1:200 | 500$ |
| 1:400 | 250$ |
| 1:500 | 200$ |
Fxpulp has provided investors a cutting edge revolutionary offer: unlimited leverage
Do you know what does this mean??
It means you don’t have to deposit money to be able to trade or to avoid a margin call, all you have to do is to send the money you are willing to risk and that’s it, and you will be able to trade freely whatever product you want, with the size you want, and you don’t need a penny to cover it.
We at FXPULP believe that taking a good investment decision and make some money out of it is a very difficult thing to do in these markets; it needs a lot of reading, following up and analysis, which is why we believe that the profits you make are yours, and it’s not for anyone else to share with you, you bear all the risk, and that’s why you should enjoy all the profits…that was the idea when we eliminated all the costs, from commissions to swaps and hidden fees, we just swept them all away so you can take all your profits, each and every pip you make in this market is yours and yours only…
What is ZERO liquidation?
Liquidation means closing all open positions when your equity goes below a certain level…your positions get liquidated when your margin level drops below 100% or 50% or any other level that brokers impose on you, which makes the chances hard for investors to benefit if the market moved back in their favor, and that’s why we offered to take this percentage to zero, so your positions stay open until your account equity drops down to zero, which will give you the full chance to benefit from your investment.
The ZERO account will set your investments free and open new horizons, ones that didn’t even exist before in the FOREX market.
- Trade freely with no restrictions.
- Your total freedom from spreads.
- Your total freedom from margin requirements.
- Your total freedom from added commissions and costs.
- Your total freedom from the fear of liquidation.
Fxpulp zero accounts trading rules & policies:
What is a spread in forex trading?
Forex brokers will quote you two different prices for a currency pair: the bid and ask price.
The “bid” is the price at which you can SELL the base currency.
The “ask” is the price at which you can BUY the base currency.
The difference between these two prices is known as the spread.
The spread is how “no commission” brokers make their money.
Instead of charging a separate fee for making a trade, the cost is built into the buy and sell price of the currency pair you want to trade.
From a business standpoint, this makes sense. The broker provides a service and has to make money somehow.
- They make money by selling the currency to you for more than they paid to buy it.
- And they also make money by buying the currency from you for less than they will receive when they sell it.
- This difference is called the spread.
It’s just like if you were trying to sell your old iphone to a store that buys used iphones. (A smartphone with only two rear cameras? Yuck!)

In order to make a profit, it will need to buy your iphone at a price lower than the price it’ll sell it for.
If it can sell the iphone for $500, then if it wants to make any money, the most it can buy from you is $499.
That difference of $1 is the spread.
So when a broker claims “zero commissions” or “no commission”, it’s misleading because while there is no separate commission fee, you still pay a commission.
It’s just built into the bid/ask spread!
How is the spread in forex trading measured?
The spread is usually measured in pips, which is the smallest unit of the price movement of a currency pair.
For most currency pairs, one pip is equal to 0.0001.
An example of a 2 pip spread for EUR/USD would be 1.1051/1.1053.

Currency pairs involving the japanese yen are quoted to only 2 decimal places (unless there are fractional pips, then it’s 3 decimals).
For example, USD/JPY would be 110.00/110.04. This quote indicates a spread of 4 pips.
What types of spreads are in forex?
The type of spreads that you’ll see on a trading platform depends on the forex broker and how they make money.
There are two types of spreads:
- Fixed
- Variable (also known as “floating”)

Fixed spreads are usually offered by brokers that operate as a market maker or “dealing desk” model while variable spreads are offered by brokers operating a “non-dealing desk” model.
What are fixed spreads in forex?
Fixed spreads stay the same regardless of what market conditions are at any given time. In other words, whether the market is volatile like kanye’s moods or quiet as a mouse, the spread is not affected. It stays the same.
Using a dealing desk, the broker buys large positions from their liquidity provider(s) and offers these positions in smaller sizes to traders.
This means that the broker acts as the counterparty to their clients’ trades.
By having a dealing desk, this allows the forex broker to offer fixed spreads because they are able to control the prices they display to their clients.
What are the advantages of trading with fixed spreads?
Fixed spreads have smaller capital requirements, so trading with fixed spreads offer a cheaper alternative for traders who don’t have a lot of money to start trading with.
Trading with fixed spreads also makes calculating transaction costs more predictable. Since spreads never change, you’re always sure of what you can expect to pay when you open a trade.
What are the disadvantages of trading with fixed spreads?
Requotes can occur frequently when trading with fixed spreads since pricing is coming from just one source (your broker).
And by frequently, we mean almost as frequently as instagram posts from kardashian sisters!
So if you try to enter a trade at a specific price, the broker will “block” the trade and ask you to accept a new price. You will be “re-quoted” with a new price.
The requote message will appear on your trading platform letting you know that price has moved and asks you whether or not you are willing to accept that price. It’s almost always a price that is worse than the one you ordered.
Slippage is another problem. When prices are moving fast, the broker is unable to consistently maintain a fixed spread and the price that you finally end up after entering a trade will be totally different than the intended entry price.
Slippage is similar to when you swipe right on tinder and agree to meet up with that hot gal or guy for coffee and realize the actual person in front of you looks nothing like the photo.
What are variable spreads in forex?
As the name suggests, variable spreads are always changing. With variable spreads, the difference between the bid and ask prices of currency pairs are constantly changing.
This means they have no control over the spreads. And spreads will widen or tighten based on the supply and demand of currencies and the overall market volatility.
Typically, spreads widen during economic data releases as well as other periods when the liquidity in the market decreases (like during holidays and when the zombie apocalypse begins).

For example, you may want to buy EURUSD with a spread of 2 pips, but just when you’re about to click buy, the U.S. Unemployment report is released and the spread rapidly widens to 20 pips!
Oh, and spreads may also widen when trump randomly tweets about the U.S. Dollar when he was still the president.

What are the advantages of trading with variable spreads?
Variable spreads eliminate experiencing requotes. This is because the variation in the spread factors in changes in price due to market conditions.
(but just because you won’t get requoted doesn’t mean you won’t experience slippage.)
Trading forex with variable spreads also provides more transparent pricing, especially when you consider that having access to prices from multiple liquidity providers usually means better pricing due to competition.
What are the disadvantages of trading with variable spreads?
Variable spreads aren’t ideal for scalpers. The widened spreads can quickly eat into any profits that the scalper makes.
Variable spreads are just as bad for news traders. Spread may widen so much that what looks like a profitable can turn into an unprofitable within a blink of an eye.
Fixed vs variable spreads: which is better?
The question of which is a better option between fixed and variable spreads depends on the need of the trader.
There are traders who may find fixed spreads better than using variable spread brokers. The reverse may also be true for other traders.
Generally speaking, traders with smaller accounts and who trade less frequently will benefit from fixed spread pricing.
And traders with larger accounts who trade frequently during peak market hours (when spreads are the tightest) will benefit from variable spreads.
Traders who want fast trade execution and need to avoid requotes will want to trade with variable spreads.
Spread costs and calculations
Now that you know what a spread is, and the two different types of spreads, you need to know one more thing…
How the spread relates to actual transaction costs.
It’s pretty easy to calculate and all you need are two things:
- The value per pip
- The number of lots you’re trading
Let’s look at an example…

In the quote above, you can buy EURUSD at 1.35640 and sell EURUSD at 1.35626.
This means if you were to buy EURUSD and then immediately close it, it would result in a loss of 1.4 pips.
To figure out the total cost, you would multiply the cost per pip by the number of lots you’re trading.
So if you’re trading mini lots (10,000 units), the value per pip is $1, so your transaction cost would be $1.40 to open this trade.

The pip cost is linear. This means that you will need to multiply the cost per pip by the number of lots you are trading.
If you increase your position size, your transaction cost, which is reflected in the spread, will rise as well.
For example, if the spread is 1.4 pips and you’re trading 5 mini lots, then your transaction cost is $7.00.
Spread definition
What is a spread?
A spread can have several meanings in finance. Basically, however, they all refer to the difference between two prices, rates or yields.
In one of the most common definitions, the spread is the gap between the bid and the ask prices of a security or asset, like a stock, bond or commodity. This is known as a bid-ask spread.
Spread can also refer to the difference in a trading position – the gap between a short position (that is, selling) in one futures contract or currency and a long position (that is, buying) in another. This is officially known as a spread trade.
In underwriting, the spread can mean the difference between the amount paid to the issuer of a security and the price paid by the investor for that security—that is, the cost an underwriter pays to buy an issue, compared to the price at which the underwriter sells it to the public.
In lending, the spread can also refer to the price a borrower pays above a benchmark yield to get a loan. If the prime interest rate is 3%, for example and a borrower gets a mortgage charging a 5% rate, the spread is 2%.
Key takeaways
- In finance, a spread refers to the difference between two prices, rates or yields
- One of the most common types is the bid-ask spread, which refers to the gap between the bid (from buyers) and the ask (from sellers) prices of a security or asset
- Spread can also refer to the difference in a trading position – the gap between a short position (that is, selling) in one futures contract or currency and a long position (that is, buying) in another
Bid-ask spread
The bid-ask spread is also known as the bid-offer spread and buy-sell. This sort of asset spread is influenced by a number of factors:
- Supply or "float" (the total number of shares outstanding that are available to trade)
- Demand or interest in a stock
- Total trading activity of the stock
For securities like futures contracts, options, currency pairs and stocks, the bid-offer spread is the difference between the prices given for an immediate order – the ask – and an immediate sale – the bid. For a stock option, the spread would be the difference between the strike price and the market value.
One of the uses of the bid-ask spread is to measure the liquidity of the market and the size of the transaction cost of the stock. For example, on jan. 8, 2019 the bid price for alphabet inc., google's parent company, was $1,073.60 and the ask price was $1,074.41. The spread is 80 cents, or $.80. This indicates that alphabet is a highly liquid stock, with considerable trading volume.
Spread trade
The spread trade is also called the relative value trade. Spread trades are the act of purchasing one security and selling another related security as a unit. Usually, spread trades are done with options or futures contracts. These trades are executed to produce an overall net trade with a positive value called the spread.
Spreads are priced as a unit or as pairs in future exchanges to ensure the simultaneous buying and selling of a security. Doing so eliminates execution risk wherein one part of the pair executes but another part fails.
Yield spread
The yield spread is also called the credit spread. The yield spread shows the difference between the quoted rates of return between two different investment vehicles. These vehicles usually differ regarding credit quality.
Some analysts refer to the yield spread as the “yield spread of X over Y.” this is usually the yearly percentage return on investment of one financial instrument minus the annual percentage return on investment of another.
Option-adjusted spread
To discount a security’s price and match it to the current market price, the yield spread must be added to a benchmark yield curve. This adjusted price is called option-adjusted spread. This is usually used for mortgage-backed securities (MBS), bonds, interest rate derivatives and options.
For securities with cash flows that are separate from future interest rate movements, the option-adjusted spread becomes the same as the Z-spread.
Z-spread
The Z-spread is also called the Z SPRD, yield curve spread and zero-volatility spread. The Z-spread is used for mortgage-backed securities. It is the spread that results from zero-coupon treasury yield curves which are needed for discounting pre-determined cash flow schedule to reach its current market price. This kind of spread is also used in credit default swaps (CDS) to measure credit spread.
Bid-ask spreads in the foreign currency exchange market
The bid-ask spread (informally referred to as the buy-sell spread) is the difference between the price a dealer will buy and sell a currency. However, the spread, or the difference, between the bid and ask price for a currency in the retail market can be large, and may also vary significantly from one dealer to the next.
Understanding how exchange rates are calculated is the first step to understanding the impact of wide spreads in the foreign exchange market. In addition, it is always in your best interest to research the best exchange rate.
Key takeaways
- The bid-ask spread (or the buy-sell spread) is the difference between the amount a dealer is willing to sell a currency for versus how much they will buy it for.
- Exchange rates vary by dealer, so it's important to research the best rate before exchanging any currency.
Bid-ask spreads in the retail forex market
The bid price is what the dealer is willing to pay for a currency, while the ask price is the rate at which a dealer will sell the same currency.
For example, ellen is an american traveler visiting europe. The cost of purchasing euros at the airport is as follows:
The higher price (USD 1.40) is the cost to buy each euro. Ellen wants to buy EUR 5,000, so she would have to pay the dealer USD 7,000.
Suppose also that the next traveler in line has just returned from her european vacation and wants to sell the euros that she has left over. Katelyn has EUR 5,000 to sell. She can sell the euros at the bid price of USD 1.30 (the lower price) and would receive USD 6,500 in exchange for her euros.
Because of the bid-ask spread, the kiosk dealer is able to make a profit of USD 500 from this transaction (the difference between USD 7,000 and USD 6,500).
When faced with a standard bid and ask price for a currency, the higher price is what you would pay to buy the currency and the lower price is what you would receive if you were to sell the currency.
Direct and indirect currency quotes in forex markets
A direct currency quote, also known as a “price quotation,” is one that expresses the price of a unit of foreign currency in terms of the domestic currency. An indirect currency quote, also known as a “volume quotation,” is the opposite of a direct quote. An indirect currency quote expresses the amount of foreign currency per unit of domestic currency.
Most currencies are quoted in direct quote form (for example, USD/JPY, which refers to the amount of japanese yen per one U.S. Dollar). The currency to the left of the slash is called the base currency and the currency to the right of the slash is called, the counter currency, or quoted currency.
Commonwealth currencies
Commonwealth currencies such as the british pound and australian dollar, as well as the euro, are generally quoted in indirect form (for example, GBP/USD and EUR/USD, which refer to the amount of US dollars per one british pound and per one euro).
Consider the canadian dollar. In canada, this quotation would take the form of USD 1 = CAD 1.0750. This represents a direct quotation, since it expresses the amount of domestic currency (CAD) per unit of the foreign currency (USD). The indirect form would be the reciprocal of the direct quote, or CAD 1 = USD 0.9302.
Next, consider the british pound. In the united kingdom, this quotation would take the form of GBP 1= USD 1.700. This represents an indirect quotation since it expresses the amount of foreign currency (USD) per unit of domestic currency (GBP). The direct form of this quote would be USD 1 = GBP 0.5882.
Understanding how currencies are quoted
When dealing with currency exchange rates, it's important to have an understanding of how currencies are quoted.
Suppose there is a canadian resident who is traveling to europe and needs euros. The exchange rates in the forex market are approximately USD 1 = CAD 1.0750, and EUR 1 = USD 1.3400. That means the approximate EUR/CAD spot rate would be EUR 1 = CAD 1.4405 (1.3400 x 1.0750). A currency dealer in canada might quote a rate of EUR 1 = CAD 1.4000 / 1.4800, which means that you would pay 1.48 canadian dollars to buy one euro and would receive 1.40 canadian dollars if you sold one euro.
The calculation would be different if both currencies were quoted in direct form. If the approximate spot rate for the japanese yen is USD 1 = JPY 102, this is how you would calculate the price of yen in canadian dollars:
In general, dealers in most countries will display exchange rates in direct form, or the amount of domestic currency required to buy one unit of a foreign currency.
How to calculate cross-currency rates
When dealing with cross currencies, first establish whether the two currencies in the transaction are generally quoted in direct form or indirect form. If both currencies are quoted in direct form, the approximate cross-currency rate would be calculated by dividing "currency A" by "currency B."
If one currency is quoted in direct form and the other in indirect form, the approximate cross-currency rate would be "currency A" multiplied by "currency B."
When you calculate a currency rate, you can also establish the spread, or the difference between the bid and ask price for a currency. More importantly, you can determine how large the spread is. If you decide to make the transaction, you can shop around for the best rate.
Exchange rates vary by dealer
Rates can vary between dealers in the same city. Spending a few minutes online comparing the various exchange rates can potentially save you 0.5% or 1%.
Airport kiosks have the worst exchange rates, with extremely wide bid-ask spreads. It's possible to receive 5% less of the currency you are buying. It may be preferable to carry a small amount of foreign currency for your immediate needs and exchange bigger amounts at banks or dealers in the city.
Some dealers will automatically improve the posted rate for larger amounts, but others may not do so unless you specifically request a rate improvement. If you haven’t had the time to shop around for the best rates, research ahead of time so you have an idea of the spot exchange rate and understand the spread. If the spread is too wide, consider taking your business to another dealer.
The bottom line
Wide spreads are the bane of the retail currency exchange market. However, you can mitigate the impact of these wide spreads by researching the best rates, foregoing airport currency kiosks and asking for better rates for larger amounts.
Sports betting 101: what does the point spread mean, and why do people bet it?
As a fan, you don’t care if your team wins by a point or 100. A win is a win, though that 100-point win would be a little easier on the nerves.
In sports betting, how much a team wins by is usually all that matters.
The most popular way to bet for the two most popular sports, basketball and football, is with the point spread, also known as the “side.” most baseball, hockey and soccer bets are on the moneyline, which is betting on a team to win straight up with adjusted odds. Football and basketball have moneyline bets available too, but most people will take the point spread.
The concept can be a bit confusing if you’ve never dabbled in sports betting before.
Why bet with the point spread?
The point spread was created to attract more action on a game. When the san francisco 49ers are expected to blow out the arizona cardinals, it’s not enticing to lay $300 to win $100 on a moneyline. But when the 49ers are 11-point favorites and each side is -110 odds? That’s much easier.
In that example, the 49ers are spotting the cardinals 11 points before the game starts, at least for bettors. The 49ers have to win by 12 or more points to cover the spread. If the cardinals win or lose by 10 or less, that side wins the bet. If the game lands on 11, like a 21-10 49ers win, it’s a push and all bets are refunded. If you see a -11 that means that team is favored, and +11 means you’re taking the underdog.
Nothing sharpens your math skills better than trying to figure out how big your lead as a bettor is if you have a 22.5-point basketball underdog that is losing 90-72.
The problem with the point spread can be when a team — which really doesn’t care that you bet the favorite at -11 — has a 14-point lead but gives up a meaningless score at the end to win by only seven points. They’re still happy with the win. You, as a bettor, are not.
Point spreads lead to bad beats
The most infamous example of a bad beat with the point spread probably came in the 2004 final four at the NCAA men’s basketball tournament.
Duke was a 2.5-point underdog against uconn. The huskies rallied late and took a 79-75 lead on a free throw with 3.2 seconds left. The game itself was over; duke couldn’t score twice in a few seconds. But duke guard chris duhon pulled up for a running 3-pointer just over the half-court line and banked it in at the buzzer. Duke lost 79-78, but bettors who had duke and 2.5 points won. March madness is a huge event for bettors, and reports at the time estimated that duhon’s “meaningless” shot resulted in a $30 or $40 million swing in nevada. Uconn players celebrated at the final buzzer. Uconn bettors doubled over in pain. That’s the difference between betting the moneyline and the point spread.
Baseball and hockey have point spreads too, the “run line” in baseball and “puck line” in hockey. It’s generally 1.5 with odds adjusting accordingly. Taking a big baseball favorite at -1.5 runs can make the odds more palatable. Of course, betting the new york yankees at -1.5 to bring down the odds from -190 to -110 isn’t too fun when they win 4-3 and you don’t cash a bet.
Betting on the point spread is the most common way to wager on sports. And the first time you take a favorite that wins the game but doesn’t cover the spread, you’ll understand every bettor’s heartbreak.
Zero pip spread forex brokers
Once the technology-driven trading environment appeared and showed its growing demand along with increasing trader’s awareness, many of the brokers and trading providers included into their offerings low-cost solution.
Within the market there are situations happening while the intensity on both buy and sell orders are in high demand, which means that the spread or difference between the prices dropping to 0. Thus, the spreads will start from 0 pips through the received interbank quotes, while trading costs are most commonly charged by the fixed commission per trade.
- The zero spread forex brokers are typically NDD, STP or ECN companies that provides direct access to the market and deep liquidity.
- That’s definitely obvious that zero spread reduces the trading costs and are useful for scalpers, high-volume traders and those who trade with expert advisors.
However, it is remaining recommended to more experienced or professional traders engage in these types of accounts, as it’s necessary to understand financial markets and the trading process itself deeply. Apart from that it, in order to perform successful operations the choice of trustful broker remains as paramount, do not get allured by various allegedly attractive 0 spread opportunities from brokers with non-confirmed status or with no regulation or offshore nature. Unfortunately, many of those “technological driven” companies turn out to be scams and only well-regulated broker are able to provide true zero spread environment.
So, let's see, what we have: zero spread accounts allow you to trade with 0% between the bid and ask price. Instead of making money on the spread, brokers with zero spread accounts typically charge a commission, allowing you to better predict the cost of your trades. Here's a comparison of the top forex brokers with zero spread accounts in 2021 at broker 0.1 spread means
Contents of the article
- Top forex bonuses
- Compare zero spread brokers
- We found 5 broker accounts (out of 147)...
- Thinkmarkets
- Using zero spread accounts in forex trading
- Advantages of zero spread accounts
- Disadvantages of zero spread accounts
- How to compare brokers that offer zero spread...
- Conclusion
- Why choose thinkmarkets for zero spread...
- A comparison of thinkmarkets
- Frequently asked questions
- Related pages
- Ready to find your broker?
- What does a forex spread tell traders?
- What is a spread in forex trading?
- How to calculate the forex spread and costs
- Understanding a high spread and a low spread
- What is a spread and why does it matter?
- It’s very important to understand spreads in the...
- Cost for each...
- How does the spread...
- Suggested articles
- Know your spread
- How to select the best...
- Beware of brokers offering zero spread!
- Newfx pulppromotion– trade with ZERO spread AND...
- Suggested articles
- What is a spread in forex trading?
- How is the spread in forex trading measured?
- What types of spreads are in forex?
- What are fixed spreads in forex?
- What are the advantages of trading with...
- What are the disadvantages of trading with fixed...
- What are variable spreads in forex?
- What are the advantages of trading with variable...
- What are the disadvantages of trading with...
- Fixed vs variable spreads: which is better?
- Spread costs and calculations
- Spread definition
- What is a spread?
- Bid-ask spread
- Spread trade
- Yield spread
- Option-adjusted spread
- Z-spread
- Bid-ask spreads in the foreign currency exchange...
- Bid-ask spreads in the retail forex market
- Direct and indirect currency quotes in forex...
- Understanding how currencies are quoted
- How to calculate cross-currency rates
- Exchange rates vary by dealer
- The bottom line
- Sports betting 101: what does the point spread...
- Why bet with the point spread?
- Point spreads lead to bad beats
- Zero pip spread forex brokers
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.